迭代器简介绍
迭代器就像是一个”指针”,指向容器(比如vector、list)中的某个元素。通过迭代器,我们不仅可以访问和修改容器中的元素,还能在容器中自由移动(前进或后退)。
简而言之,迭代器充当着容器与算法之间的纽带,让你无需了解容器内部实现细节,就能方便地遍历和操作容器元素。
迭代器可以透明地访问容器内部的元素的值。
STL中提供的一些迭代器:
const_iterator:常量的正向迭代器,只能读,不能通过该迭代器修改值iterator:普通的正向迭代器const_reverse_iterator:常量的反向迭代器,只能读,不能写reverse_iterator:普通的反向迭代器
以下是迭代器使用的样例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| vector <int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
vec.push_back(rand() % 100 + 1);
}
vector<int>::iterator it1= vec.begin();
for (; it1 != vec.end(); ++it1)
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
if (*it1 % 2 == 0)
{
*it1 =0;
}
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::const_iterator it2 = vec.begin();
for (; it2 != vec.end(); ++it2)
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::reverse_iterator it3 = vec.rbegin();
for (;it3!=vec.rend();++it3)
{
cout << *it3 << " ";
if (*it3 == 0)
{
*it3 = 1;
}
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::const_reverse_iterator it4 = vec.rbegin();
for (; it4 != vec.rend(); ++it4)
{
cout << *it4 << " ";
}
|
自定义实现迭代器
迭代器一般嵌套实现在容器内部,在上一篇实现容器配置器中我们实现了自定义的vector,本节我们继续在此基础上探索迭代器的实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class iterator
{
public:
iterator(T* p=nullptr) :_p(p) {}
bool operator!= (const iterator& it) const
{
return _p != it._p;
}
void operator++()
{
++_p;
}
T& operator*() { return *_p; }
const T& operator*()const { return *_p; };
private:
T* _p;
};
iterator begin() { return iterator(_first); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_last); }
|
将上述的iterator添加到自定义的vector内部后 ,就可以通过迭代器遍历自定义的vector内部元素了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| int main()
{
vector <int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
vec.push_back(rand() % 100 + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
{
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it = vec.begin();
for (; it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int val : vec)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
|
迭代器失效
迭代器为什么会失效?
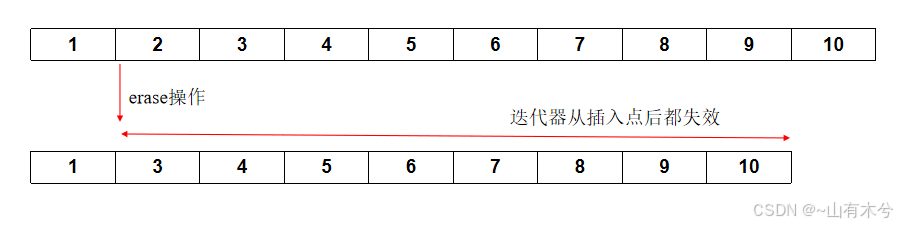
- 当容器调用erase方法后,当前位置到容器末尾的所有迭代器全部失效了
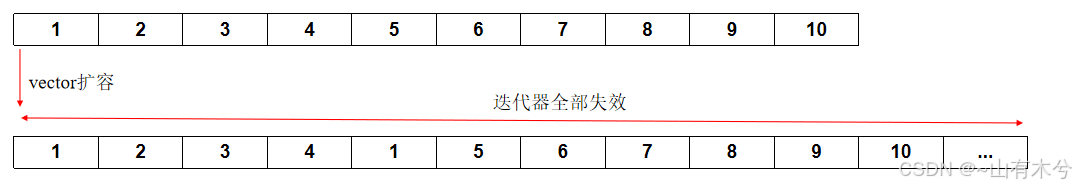
- 当调用insert方法后,分为两种情况
- 如果没有扩容操作,当前插入点到末尾的所有迭代器全部失效
- 如果有扩容操作,容器全部失效
迭代器失效部分的代码比较复杂,我这里就使用stl中的vector进行记录
插入操作导致的迭代器失效:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| vector<int> vec;
vec.reserve(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
if (*it % 5 == 0)
{
vec.insert(it, *it - 1);
}
}
|
![image]()
执行这里代码是异常退出的;
![image]()
删除操作导致的迭代器失效:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| vector<int> vec;
vec.reserve(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
vec.erase(it);
}
}
|
![image]()
解决迭代器失效问题的方法
当容器(如vector、list、map等)在进行插入或删除操作时,会导致迭代器失效。那如何解决上述提到的迭代器失效问题呢?
其实erase函数和insert函数返回了对应的一个迭代器,当进行插入或者删除后,会返回下一个元素的迭代器。以下是详细分析:
- erase函数的正确用法
- 标准库中的erase函数会返回被删除元素的下一个有效迭代器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| vector<int> vec;
vec.reserve(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); )
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it=vec.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " " ;
}
|
![image]()
- insert函数的正确用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| vector<int> vec;
vec.reserve(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
if (*it % 5 == 0)
{
it=vec.insert(it,1);
++it;
}
}
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " " ;
}
|
![image]()
总结
迭代器失效看起来很复杂,但只要记住几个简单的规则,就能轻松避开这个坑:
vector: 插入或删除元素后,该位置及其后面的迭代器都会失效;如果重新分配内存,所有迭代器都会失效。
list/forward_list: 只有被删除元素的迭代器会失效。
map/set/multimap/multiset: 只有被删除元素的迭代器会失效。
unordered_map/unordered_set: 插入操作可能导致所有迭代器失效(rehash);删除操作只会导致被删除元素的迭代器失效。
迭代器失效:99%的C++程序员都会踩的坑 !
$share-item-width = 1.8rem
.post-share-container {
flex-shrink 0
.share-list-wrap {
display flex
justify-content flex-end
.share-item {
width $share-item-width
height $share-item-width
margin-left 0.5rem
padding 0.4rem
border-style solid
border-width 0.1rem
border-radius 50%
cursor pointer
transition-t("background", "0", "0.3", "ease")
i {
color inherit
font-size 1rem
}
&.qq {
color var(--keep-primary-color)
border-color var(--keep-primary-color)
&:hover {
color var(--background-color-1)
background var(--keep-primary-color)
}
}
&.wechat {
color var(--keep-success-color)
border-color var(--keep-success-color)
img {
filter brightness(1) !important
&[lazyload] {
&::before {
background #fff !important
}
}
}
&:hover {
color var(--background-color-1)
background var(--keep-success-color)
}
}
&.weibo {
color var(--keep-danger-color)
border-color var(--keep-danger-color)
&:hover {
color var(--background-color-1)
background var(--keep-danger-color)
}
}
}
}
}
if (hexo-config('comment') && hexo-config('comment.enable') == true && hexo-config('comment.use')) {
if (hexo-config('comment.use') == "valine") {
@import "./valine.styl"
}
else if (hexo-config('comment.use') == "gitalk") {
@import "./gitalk.styl"
}
else if (hexo-config('comment.use') == "twikoo") {
@import "./twikoo.styl"
}
else if (hexo-config('comment.use') == "waline") {
@import "./waline.styl"
}
}
.comments-container {
display inline-block
width 100%
margin-top var(--component-gap)
.comment-area-title {
width 100%
color var(--text-color-3)
font-size 1.38rem
line-height 2
i {
color var(--text-color-3)
}
+keep-tablet() {
font-size 1.2rem
}
}
.configuration-items-error-tip {
display flex
align-items center
margin-top 1rem
color var(--text-color-3)
font-size 1rem
i {
margin-right 0.3rem
color var(--text-color-3)
font-size 1.2rem
}
}
.comment-plugin-fail {
display none
flex-direction column
align-items center
justify-content space-around
width 100%
padding 2rem
.fail-tip {
color var(--text-color-3)
font-size 1.1rem
}
.reload {
margin-top 1rem
}
}
.comment-plugin-loading {
flex-direction column
padding 1rem
color var(--text-color-3)
.loading-icon {
color var(--text-color-4)
font-size 2rem
}
.load-tip {
margin-top 1rem
color var(--text-color-4)
font-size 1.1rem
}
}
}